Good exercises for cervical osteochondrosis of the spine
Important! Doctors in shock: "An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists..." ...
Osteochondrosis is considered one of the most common diseases of the joints. It is a complex of dystrophic processes in the articular cartilage of the spinal column. There are osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions. Most often, the disease affects cartilage and intervertebral discs in the neck area. This part of the spinal column is considered the most mobile and most unprotected. It has many nerve knots and vessels, the vertebrae themselves are small and surrounded by weak muscles.
The first signs of malaise can appear in 25-30 years. Such a “young” age of the disease is explained by a sedentary lifestyle, office work. As a rule, the pathology develops slowly and at first occasionally declares itself with a feeling of discomfort and implicit pain sensations. Therefore, it is recommended to regularly perform special exercises as a prevention of cervical osteochondrosis.
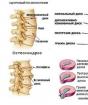
The structure of the spine
The spine is one of the most important elements of the human skeleton. It is thanks to the features of its structure that bipedalism is ensured. It has the shape of the English letter S, which gives it flexibility and also allows it to perform a shock-absorbing function while walking and running. Inside the spinal column are the spinal cord and nerve roots that regulate the work of all organs, muscles and body systems. The spine consists of five sections, the upper of which is the cervical.
It includes seven vertebrae, firmly interconnected. The two very first vertebrae are distinguished by a special anatomy, unlike the others, and are called "atlas" and "axis". The atlas is devoid of a vertebral body and is formed by the anterior and posterior arches connected by a bony thickening. The axis has a process in the form of a tooth, fixed by ligaments in the opening of the atlas, allowing rotation. The transverse vertebral processes contain blood vessels that supply blood to the brain stem, occipital lobe of the cerebral hemisphere, and cerebellum.
The essence of the disease
The development of the disease occurs when the intervertebral pulp, which has a soft structure and absorbs friction between the vertebrae, is converted into a ossified surface. In this case, the nerve roots and blood vessels are involved in the change. Osteochondrosis is often confused with other diseases, since it is characterized by dizziness, headaches, pressure surges and nausea inherent in diseases of the cardiovascular system.

The disease can have a dual clinical nature:
- physiological changes associated with age. With them, natural aging of cartilage tissue is observed, due to neurological and endocrine processes. Almost do not manifest themselves or only in case of irritation of nerve endings;
- pathological disorders, entailing the destruction of intervertebral structures, nerve and vascular nodes. The most common cause is an unhealthy lifestyle. Pathogenesis always means aging of the organ, even in young ones, and leads to the appearance of microcracks, weakening of the vertebrae and the spinal column as a whole.

Pathology is accompanied by:
- accumulation of calcium salts;
- pressing one vertebra into another;
- gradual deformation of the vertebrae - spondylosis;
- ossification of the ligaments.
In both situations, the sooner you seek qualified help, the faster you can stop degeneration. Exercises for the neck with osteochondrosis are especially successful with this.
Causes
Prerequisites for development are:
- violation of metabolic processes in the neck;
- incorrect posture, scoliosis, rheumatism, flat feet;
- heavy physical work;
- little activity;
- neck and back injuries;
- obesity;
- sports;
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious diseases;
- hypothermia;
- stress.

All these causes in the majority put pressure on the cervical region, which causes muscle spasms. As a result, destabilization of blood circulation and metabolism occurs, the cartilage does not receive the necessary nutrition and gradually deforms. The distance between the intervertebral discs is reduced, they begin to shift beyond the spine.
Complications
Through the neck passes the spinal cord, nerve roots and vertebral artery, which is responsible for the blood supply to the back of the brain, medulla oblongata and cerebellum. With osteochondrosis, the artery is squeezed and normal blood circulation is disturbed. In severe stages, this can have a negative impact on vision, hearing, and even provoke a stroke. Measures not taken in time are fraught with protrusion of the intervertebral disc, followed by a hernia.
Stages of destruction
The disease has several phases, which are determined depending on the degree of damage to the joints:

- At the initial stage, the symptoms are subtle and insignificant. Basically, these are muscle spasms and mild pain in the nerve roots. Therapeutic measures are represented by a vitamin complex, physiotherapy and exercise therapy. You can use ointments, they are quite effective
- At the second stage, protrusion occurs - the bulging of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal, without violating the integrity of the fibrous ring. The gaps between the vertebrae decrease, pinching of the nerve endings may occur. There is a pain syndrome.
- The third degree is characterized by exacerbated symptoms. The pain becomes intense, spreading to the area of the shoulders and arms. On palpation, the pain is sharp and strong. There is numbness in the fingers and muscles. Articulations periodically fetter, motor function is rapidly deteriorating.
- At the fourth stage, the intervertebral disc is completely deformed and connective tissue remains in its place. Dizziness, tinnitus are added to the pain, coordination of movements is disturbed.
Symptoms
Signs manifest themselves in different ways, it depends on the type of damaged vertebrae. The main symptom is pain, affecting not only the neck, but also the upper body. In addition to it, there is a crunch when a person moves his neck, his vision and hearing decrease, and blood pressure rises. All patients, without exception, note weakness in the upper and lower extremities.

Syndromes:
- radicular;
- hypertensive;
- arterial;
- neck migraine.

With radicular syndrome - compression of the roots of the spinal cord - symptoms of a neurological orientation appear:
- pronounced pain in the neck (cervicalgia), spreading to the forearm and humerus;
- pain in the hand;
- crunching and clicking;
- pain radiating to the ear after a long stay in one position;
- sensation of a lump in the throat;
- labored breathing;
- numbness of the tongue and upper limbs;
- weakness, tinnitus;
- hearing and vision problems.
A patient experiencing radicular syndrome feels "goosebumps" on the skin, tingling. The skin becomes rough and becomes pale. There is a slight swelling.

Hypertension syndrome is expressed by an increase in intracranial pressure. The patient has the impression of "bursting" the head, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. In the acute stages, fever and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may appear, which is detected during laboratory analysis.
Arterial or vertebral artery syndrome, declares itself already at the first stage of the disease. It is characterized by throbbing or burning pain in the upper part of the head, which lasts constantly or comes in fits. With a long stay in an uncomfortable position, pain intensifies, they are joined by dizziness, disruption of the vestibular apparatus, "fog" before the eyes, and decreased visual acuity.

With cervical migraine, sympathetic nodes are irritated, as a result of which the reactivity of the cerebral vessels and blood circulation are disturbed. This can lead to oxygen starvation of brain cells, mental disorders, episyndrome - a short-term loss of consciousness with tension throughout the body. This syndrome contributes to the development of hypertension, which is accompanied by tachycardia, noise in the head and ringing in the ears.

In addition to the above signs, patients have a heart rhythm disturbance, swelling under the eyes after sleep. Pathology often provokes a disease such as vegetovascular dystonia, when the vascular arteries passing along the sides of the spine are pinched.
If the diagnosis is cervical osteochondrosis at the initial stage, you should not waste precious time and start doing exercises for it right now.
Diagnostics
When the first signs appear, you should immediately go to the clinic to see a neurologist. He conducts an examination and questioning and gives a referral for x-rays. Until recently, these actions were enough to make a diagnosis, but radiography does not give a complete picture - it is not possible to determine from the picture how much the disease has developed. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are considered the most informative methods. After that, the patient continues treatment with a narrow specialist - a vertebrologist or a vertebroneurologist.
Treatment
Therapeutic activities are presented in three areas:
- conservative (drug and therapeutic);
- surgical intervention;
- combination of the first and second.
![]()
Depending on the degree of damage to the cartilage and intervertebral discs, as well as the condition - exacerbation or remission, an individual treatment program is developed. A competent doctor will select the appropriate technique, including exercises for cervical osteochondrosis at home and massage, which will greatly facilitate well-being. If there are long-term degenerative processes, it is recommended to be examined in a hospital or on an outpatient basis.
Medical method
- Analgesics, NSAIDs. These are pain relief pills. Their downside is that they negatively affect the digestive tract. This shortcoming is deprived of drugs of the new generation.
- Chondroprotectors. They contribute to the restoration of cartilage tissue due to chondrotin and hyaluronic acid. The course of admission lasts six months or more.
- Blockades. If the pain is too strong and prescribed medications do not cope with them, injections of hydrocortisone, prednisolone or flosterone are given. These are hormonal drugs, the interval between injections should be at least 20 days.
- Muscle relaxants. They affect muscle tone, relieve spasms.
- Ointments for external use.
A set of exercises for the cervical region
Exercise therapy is indicated for all patients, except for those who have recently undergone surgery. Its goal is to restore the normal nutrition of the cartilage and improve the patient's condition. There are many techniques, but they are all based on the principle of restoring blood supply to the damaged area and developing muscles.
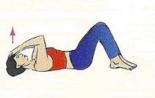
Complex 1.
- Stand up, lower your arms along the body. The back is as straight as possible. Slowly and carefully turn your head to the side to 90 degrees. Start with a small amplitude of rotation, then increase the angle.
- The starting position is the same. Relax your neck muscles, lower your head and touch your chin to your chest. If it doesn't work the first time, no big deal. Don't make an effort.
- Relax the collar area and shoulders. Slowly tilt your head back. Movements should be smooth.
These are effective exercises for cervical osteochondrosis, which restore flexibility and elasticity to the spine, tone muscles.

Complex 2.
- Can be sitting or standing. Straighten your neck, relax your upper body muscles. Touch your forehead, then make a repulsive movement with your head.
- The same thing, only with a palm to the temple.
- Sit down. Keep your back straight, do not strain your muscles. Raise your shoulders to your ears, hold for 5-20 seconds, lower.
- Stand up, arms raised to the sides. Rotate first with one limb, then the other.
- Light self-massage of the neck.
- Standing or sitting. Shake your head without making a sharp nod, as if in agreement.
- The starting position is the same. Now shake your head in imitation of rejection.
This complex is suitable for patients who are undergoing an exacerbation.

Complex 3.
- Stand up, feet shoulder width apart. Stretch your body forward with your arms outstretched. Make a mill.
- Stay standing or sit down. Keep your back straight. Tilt your head to your shoulder, trying to touch it with your ear.
- Shake your head as if showing yes and no.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis are quite simple, but their regular performance will positively affect the course of the disease.
Physiotherapy procedures
Physical procedures are designed to enhance the effect of drugs, reduce pain and accelerate regenerative processes.

Often used:
- electrophoresis;
- ultrasound;
- magnetotherapy;
- laser therapy.
Massage
Massages are necessary for this disease, but they should be done by a specialist, since inept or erroneous actions can provoke deterioration. Preference is given to the classic type of massage, including stroking, kneading and rubbing. If the pain is localized on one side, then the session begins with a healthy part of the collar zone.
Prevention
The disease can be prevented or stopped if you follow simple rules:

- sports and active lifestyle;
- a variety of diet foods containing magnesium and calcium, the exclusion of salty, spicy, smoked and spices;
- if professional activity requires perseverance, you need to interrupt several times and do a little warm-up;
- for sleep, choose an orthopedic mattress and a comfortable pillow.
Check out the reviews of patients who have undergone treatment abroad. In order to receive information about the possibility of treatment for your case, leave us a request for treatment at this link.
Be sure to consult your doctor before treating diseases. This will help to take into account individual tolerance, confirm the diagnosis, make sure the treatment is correct and exclude negative drug interactions. If you use prescriptions without consulting a doctor, then this is entirely at your own risk. All information on the site is presented for informational purposes and is not a medical aid. You are solely responsible for the application.