Features, symptoms, development and diagnosis of pain in the heart with osteochondrosis
Pain in the heart is the most common complaint of patients who have crossed the forty-year milestone. The cause of an unpleasant symptom may be a heart attack, angina pectoris, but sometimes pain does not depend on pathological processes in the heart muscle.
If, as part of the diagnosis, no violations of the cardiovascular system were detected, then osteochondrosis can be suspected. It has been established that aching, stabbing, pulling pain in osteochondrosis can radiate to the heart. It does not threaten the life of the patient, but requires urgent treatment. It is not easy to determine false pain in the heart with osteochondrosis if you do not know the distinctive symptoms.
The disease is diagnosed in middle-aged and elderly patients. This age group is also prone to the development of heart attack and angina pectoris, which complicates the diagnosis of the disease.
Even highly qualified doctors cannot always distinguish pain in the heart with osteochondrosis from cardiac pathologies.
Features of pain in the heart with osteochondrosis:
- Cardialgia lasts for several weeks, months;
- The pain is accompanied by rhythm disturbance;
- Pain syndrome occurs acutely and gradually increases, subsides after 3-4 days;
- Possible tingling of the fingers and numbness of the skin;
- The attack is not accompanied by fear of death;
- Increased pain in the supine position;
- Feeling of warmth in the chest;
- During the ECG, there are no pathologies of the heart;
- The use of cardiac drugs does not bring relief, pain is stopped only by analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- The pain extends along the upper limbs, may affect the fingers;
- It is possible to increase the pain syndrome with movements of the head, hands.
During a medical examination, there is pain in the processes of 5-7 cervical vertebrae, weakness of the little finger on the left hand, impaired movement during extension and flexion of the arm. An exacerbation of osteochondrosis can provoke any careless movements of the spinal column: a sharp wave of the arms, turning the head and body, tilting, coughing or sneezing. Pain often occurs after a long stay in a static position, for example, in a dream.
During an attack of angina, the patient notes intense cutting pain in the chest. A characteristic feature is irradiation to the left hand.
Pain syndrome can occur during sleep, but is usually associated with physical activity, neuropsychic overstrain. A person has thoughts of approaching death. The pain syndrome lasts a couple of minutes, is easily stopped with the help of nitroglycerin and validol. The intensity does not change depending on the load on the spinal column. During the electrocardiogram, the doctor fixes violations.
The main mechanisms of the development of pain in osteochondrosis

The conducted studies made it possible to reveal how heart pain develops in this pathology of the spine:
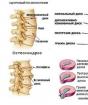
- The disease is characterized by the appearance of pathological growths on the intervertebral discs. This eventually causes irritation of the roots of the spinal cord. Numerous signals first through the nerves of the autonomic nervous system penetrate into the stellate section, which also innervates the heart muscle. As a result, the heart with osteochondrosis can hurt due to violations of its connection with the brain.
- With possible violation of the connection of the tissues of the shoulder girdle with the central nervous system. Which leads to an increase in impulses that come from the heart muscle. This signal is perceived by the brain as pain.
Changes in the cardiovascular system in the pathology of the spine
 Osteochondrosis has a negative effect on the heart, increasing the load. As a result, there are numerous pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Diseases of the spine, which are accompanied by degenerative processes, can lead to compression of the vertebral artery. Bone growths and spasmodic muscles infringe on the vessel, which leads to increased pressure inside it and pain in the heart. This pathological condition gradually causes tachycardia.
Osteochondrosis has a negative effect on the heart, increasing the load. As a result, there are numerous pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Diseases of the spine, which are accompanied by degenerative processes, can lead to compression of the vertebral artery. Bone growths and spasmodic muscles infringe on the vessel, which leads to increased pressure inside it and pain in the heart. This pathological condition gradually causes tachycardia.
Characteristic signs of tachycardia in degenerative pathologies of the spine:
- Able to occur in a calm state;
- The pulse quickens with increasing load on the spinal column;
- Saved sinus heart rate;
- Tachycardia stops after osteochondrosis therapy.
Interruptions in the heart with osteochondrosis are the development of arrhythmia and extrasystole. The latter pathology is a violation of the rhythm of heart contractions due to premature excitation of the myocardium or part of it. Contractions come from different parts of the heart muscle, although normally the impulse should originate in the sinus node.
Extrasystole is diagnosed in the later stages of osteochondrosis. Prior to this, heart rhythm disturbances are temporary: with increased load, sudden movements, when the nerve root is pinched. This is associated with an insufficient supply of oxygen to the heart, so it is further reduced. In the case of persistent extrasystole, the risk of hypoxic changes in the myocardium increases.
Arrhythmia is noted in thoracic osteochondrosis, when the intervertebral discs fall out and pinch the nerve roots. If the cardiac nerve is compressed, the synchrony of heart contractions will be disturbed.
Doctors also proved the inverse relationship: an increase in the size of the heart leads to metabolic disorders in the spine, leading to the development of osteochondrosis.
The main symptoms of disruption of the heart muscle in degenerative pathologies of the spine:
- Feeling short of breath;
- Internal discomfort;
- Pre-fainting states;
- Cardiopalmus;
- increased sweating;
- Tension in the interscapular region;
- Periodic increase in heart rate.
Cervical osteochondrosis sometimes causes the development of hypertension. The cause of the pathology will be compression of the vertebral artery and the occurrence of cerebral hypoxia. Such extreme conditions require the body to restore the nutrition of neurons by increasing the speed of blood flow. As a result, substances begin to flow into the blood, leading to an increase in pressure. The correct treatment regimen for osteochondrosis allows you to determine the relationship between the underlying disease and hypertension. In such cases, the use of antihypertensive drugs does not bring the desired result, but can also lead to severe hypoxia of the brain.
The symptoms of this pathology are:

- Drowsiness and weakness;
- confusion;
- dizziness;
- Decreased hearing and vision;
- Double vision, the appearance of "flies";
- Fainting. The symptom indicates significant hypoxia and is a protective reaction.
Numerous clinical studies have shown that osteochondrosis can lead to the development of hypertension. And also contributes to the aggravation of its course due to the body's resistance to the use of antihypertensive drugs.
Diagnostic measures
Many patients wonder how to distinguish heart pain from osteochondrosis. After all, it is important to correctly determine the pathology in pain syndrome, on which the effectiveness of therapy directly depends.
Determining the cause of cardialgia requires a comprehensive diagnosis.
 To distinguish heart pain from osteochondrosis appoint:
To distinguish heart pain from osteochondrosis appoint:
- Ultrasound diagnosis of the heart;
- Electrocardiogram;
- Measure pressure;
- Determine the level of cholesterol in the bloodstream.
If all indicators are normal, then the doctor suggests osteochondrosis. To confirm the diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging is performed. The study reveals the presence of osteophyte (growth on the spine), hernia.