Gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine

Cervical-thoracic osteochondrosis is one of the most common and unpleasant diseases of modern civilization. Statistics show that every second inhabitant of the planet is familiar with this problem.
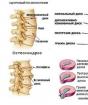
The widespread hypothesis that the cause of osteochondrosis lies in the destructive changes in the spine, the wear of aging intervertebral discs, is increasingly doubtful among professionals.
Today, the main factor provoking the clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis is the underdevelopment of the muscular corset. Today, swan gymnastics is one of the effective methods of treating cervicothoracic osteochondrosis.
Gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine

It turned out that in diseases of the spine, the back muscles are most often “to blame”. Being in a state of spasm for years and even decades, they form a muscle blockade that bleeds certain segments of the body.
All segments of the spinal column are susceptible to osteochondrosis, but most often around the vertebral muscles of the cervical and thoracic spine, which are responsible for vital organs, suffer. The matter is aggravated by chronic stress - it is in these areas that protective muscle clamps subconsciously arise.
Read also about the symptoms and methods of treatment of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis in this.
That is why special gymnastic exercises are becoming the leading method of treating cervicothoracic osteochondrosis today. Do not forget that physical therapy for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis is also an excellent means of prevention.
Helping to avoid the exacerbation of an existing process, gymnastics successfully stop those that have appeared, restoring impaired blood circulation and innervation of muscle and bone structures. Thus, the systematic implementation of the complex for the chest and neck leads to an improvement in all vital functions of the body.
To increase the effectiveness of exercises, while ensuring the safety of health, the observance of some rules will help.
Basic principles of therapeutic exercises
- Proper breathing. Using nasal breathing and lengthening the exhalation twice as compared to the inhalation, the maximum benefit from the exercise is achieved, and the body is filled with life-giving energy.
- Execution technique. A slow pace and gentle gentle movements will prevent unwanted spasms and muscle blocks in the cervicothoracic spine.
- Comfortable feeling. Classes should not be accompanied by pain and discomfort in the spine and surrounding areas of the body.
- Choice of class time. The acute period is a contraindication for gymnastics. The beginning of classes should coincide with the disappearance of pain in the spine. By continuing gymnastics in the period of remission, you can avoid another relapse.
- Gentle loads. When working with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, this is especially important - overloading the cervicothoracic areas can cause negative consequences in other parts of the spine.
- Medical control. The optimal set of exercises for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis is formed individually, based on an objective assessment of the patient's condition, given by a professional.
The main types of exercises
There are two types of exercises for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis of the spine - isometric (static) and isotonic.

Isometric and isotonic exercises for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis
essence isometric training resisting resistance. With such a load, muscle fibers are tensed without changing their length, muscle energy is used to strengthen back muscles and building new fibers. Therefore, the benefits of isometric loading are obvious, these are:
- saving time - all muscles are simultaneously included in the work within seconds,
- high efficiency - the efficiency of several minutes of static stress is equivalent to hours of isotonic training,
- minimal fatigue - the muscles get tired much less, therefore, the recovery period is reduced,
- the possibility of local training - it is better to strengthen certain muscle groups with statics,
- high degree of safety - the likelihood of injuries and stretch marks is minimized
Isometric gymnastics fills the muscles with strength, increases muscle volume and promotes muscle relaxation.
During isotonic (dynamic) exercises with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis , the muscle simultaneously with tension is reduced in length. In this case, the supply of muscle energy is spent on movement.
This type of exercise is a number of undeniable advantages:
- exercises develop tendons and stiff joints,
- increased flexibility and plasticity of muscles,
- due to dynamic contractions, tissue metabolism is accelerated many times - the muscles are more intensively supplied with blood and oxygen and are released from metabolic products.
- Static and dynamic exercises complement each other, not being interchangeable. Their alternation is necessary to restore the functions of the cervicothoracic spine.
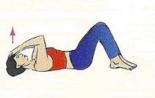
A set of exercises for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis

In this complex, the main emphasis of exercises is on the cervical spine and cervical muscles.
Practicing in front of a mirror, you can control the correct position of the head, for which at first a special bandage is used
- "Ropes". Standing straight, relax the shoulder girdle. Swinging the body from right to left, maintain maximum relaxation of the shoulders and arms.
- Put the brushes one on top of the other, place them on the occipital region, take the elbows to the sides. Press the brushes on the back of the head for three seconds, holding the head.
- Sitting on the edge of a chair, put your hands on your forehead, without throwing your head back, with your elbows abducted. Press on the forehead with your hands, trying to keep your head without moving.
- Place your fists one on top of the other, resting your chin on them. Press your fists on the chin from below, resisting with your head, hold for no more than three seconds.
- Place the palm of the right hand on the half of the head of the same name - the thumb is above the ear, the rest are directed upwards, the right elbow is moved to the side. Pressing the palm on the head, to resist.
- "Wagons". With straight arms apart, try to push the imaginary cars apart, “holding” them for three seconds. Relaxing your hands, drop them down.
- "Giri". Simulate lifting heavy weights with straight arms, aligning the spine, holding the weights in good shape for three seconds. Observe the rest time - six seconds.
Photo gallery of a set of exercises for the chest





Isometric complex for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis.
In this set of exercises, the main emphasis is on the thoracic spine and pectoral muscles:
- "Hole". In a standing position, extended along the body, imitate an attempt to get out of the pit. At the same time, pull your shoulders up and your arms down.
- "Chains". Try to break the imaginary chain with interlocked fingers, Then change the position of the hands.
- "Buddha". Bending your arms at right angles, press them to the torso and move your forearms to the sides, simulating the stretching of a rubber tourniquet. After doing three approaches, drop your hands down.
- "Dome". Standing straight, stretching the spine and looking strictly in front of you, squeeze the palms of straightened arms above your head, hold them in this state for three seconds.
- "Breast". Bring up the hands clasped behind the back, bending forward with the thoracic region. Dropping your hands, shake them, then do it again.
- Perform squeezing with the palms in front of the chest. Having made three approaches, drop the relaxed brushes down.
You can find more chest exercises.
Photo of exercises for the thoracic spine

Exercises "Dome"

Exercises "Chains"

Exercises "Fove"
Isotonic complex for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis (bias to the cervical region)
Very useful "drawing the nose" of various shapes - circles, squares, triangles and spirals. This exercise is an effective way to eliminate the subluxation of the atlas - the first vertebra.
To restore the range of motion in the cervical region, lowering your head down, smoothly slide your chin along the sternum:
- Slowly tilt your head to the side, trying to touch your shoulder with your ear.
- Turn your head in different directions, trying to touch your shoulder with your chin.
- Make rotations of the head, avoiding jerks
Exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis are important for strengthening muscles and joint structures.
Isotonic exercises for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis (bias to the thoracic region)
Alternating and simultaneously raising the shoulders helps to work out the upper thoracic spine. In the second option, simultaneously with raising one shoulder, the second goes down.
Circular movements of the arms - forward and backward - improve the function of the upper segment of the thoracic spine.
Tilts of the body to the sides with arms pressed to the body fully engage the thoracic spine. A modification of the exercise with raised arms allows you to target the middle and lower segments of the spine.
Known for its effectiveness exercise "cat". Bending the spine up (with simultaneous inhalation) and down (on exhalation) in a position on all fours.
Charging with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis video
Cervical thoracic osteochondrosis and back muscles

Gymnastic exercises aimed at the cervicothoracic spine are best performed at the same time as strengthening the back muscles.
These muscles form a muscular corset that supports the body in an upright position, makes the correct posture, giving the spine flexibility.
Strong back muscles reduce the load on the vertebrae, soften vibration during movement, preventing the development of musculoskeletal pathology.
You can strengthen your back muscles with:
- Functional training - performing balance exercises. In addition to strengthening large and small muscles, gymnastics enhances intermuscular coordination and increases the body's resistance to external influences.
- Swimming in any style. It engages all muscle groups of the back, while simultaneously stretching and relaxing the spine. Training of the back muscles in the water is very gentle and effective.
- Massage - improving muscle trophism, it also strengthens the muscle corset. During the massage, the muscles stretch and become more elastic, thereby increasing the depreciation properties of the spine.
- Yoga classes and - carefully working with the spine, they improve all aspects of body control, restoring the stability of the spine and making you forget about the manifestations of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis.
Video exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back