Electrophoresis: what is it and why is the procedure performed for infants and older children?
Children due to the imperfection of the immune system are often prone to various diseases. When treating newborns under 1 year old and older children, only the most gentle methods should be used. For babies of this age, pediatricians prescribe various physiotherapy procedures, one of which is electrophoresis. Since this method has certain contraindications, it should be used only as directed by a doctor.
Electrophoresis is an effective technique for administering drugs through the skin using electric current, which is actively used in the complex treatment of various diseases.
Electrophoresis - what is it and why is it needed?
During electrophoresis, drugs with the help of electrical impulses are converted into tiny particles, which then enter the diseased organ. With the hardware introduction of medications, most of them remain in the subcutaneous layers, and the remnants are carried with blood and lymph throughout the body.
The current discharge used during the procedure is minimal and is not capable of causing pain to a small patient. Also, electrophoresis does not harm children's health if the device is used correctly and the optimal dosages of medicines are observed. Before it is carried out, the existing contraindications must be taken into account.
Electrophoresis for children is a painless method of treating various diseases. With it, you can avoid injections associated with severe pain in infants, as well as possible complications as a result of oral medication.
Infants under 1 year of age are usually prescribed electrophoresis according to the Ratner method. This procedure is used to treat natal cerebrospinal injuries in them, for which purpose a solution of aminofillin and papaverine is administered to babies using the apparatus. For children, such manipulations are also shown to combat bronchitis, diathesis, rhinitis and other pathologies.
Indications for the procedure for infants and children older than a year

This article talks about typical ways to solve your questions, but each case is unique! If you want to know from me how to solve exactly your problem - ask your question. It's fast and free!
Due to the small number of side effects, this physiotherapy procedure in pediatrics is very popular. It contributes to the rapid cure of many diseases, even in the smallest patients.
Electrophoresis is widely used for problems in the cervical region in infants and is often prescribed when hip dysplasia is detected in babies (we recommend reading:). In addition, there is a large list of childhood diseases that are successfully cured using this physiotherapeutic method.
Electrophoresis for problems in the cervical region
With pathologies of the cervical spine, electrophoresis is indicated for small patients. It is prescribed for such manifestations as:
- boost ;
- muscle hypertonicity or hypotonicity of the arms or neck (see also:);
- birth injury;
- cerebral palsy.
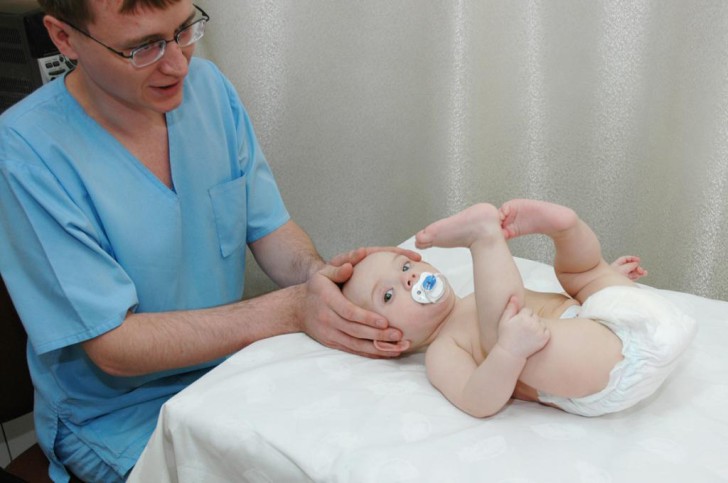 Sometimes electrophoresis is a necessary physiotherapy procedure for infants, for example, with birth injuries
Sometimes electrophoresis is a necessary physiotherapy procedure for infants, for example, with birth injuries In addition, electrophoresis is prescribed to improve the blood supply to the brain and shoulder region, to get rid of spasms of the muscles of the upper spine. During the procedure, a medicine, most often aminophylline, is injected into the neck area with the help of an electric current. The duration of the session depends on the age of the baby and the doctor's prescriptions, on average, the procedure lasts from 5 to 12 minutes.
Hip dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a serious disease, the development of which is most often associated with infection of the child by the mother during pregnancy or injury during childbirth. When making this diagnosis, babies are prescribed foot massage and electrophoresis with some kind of drug, such as aminophylline. The procedure is also carried out with the addition of calcium and chlorine to the solution, which is impregnated with contact pads.
After a course of treatment, the blood flow in the tissues around the diseased joint is normalized and its supply with microelements and nutrients is improved. The essence of electrophoresis in hip dysplasia is to place electrodes on the area of the buttocks and gluteal folds for 5-10 minutes. The duration of the course of treatment is 10-20 sessions. This physiotherapy procedure is prescribed by a doctor.
Other indications
Parents are often interested in why infants need electrophoresis. Despite the rather simple principle of action, this effective procedure is considered indispensable in identifying the following pathologies in infants:
- disorders of the musculoskeletal system;
- various heart diseases or congenital defects;
- birth trauma;
- neuralgic deviations;
- diathesis.
Electrophoresis for infants is also used to relieve pain associated with various diseases.
Indications for the appointment of the procedure in older children practically do not differ from those pathologies that electrophoresis treats in infants. Indications can also include diseases such as:
- violations of the digestive system;
- stomatitis;
- hepatitis;
- tonsillitis, otitis media, rhinitis;
- inflammatory diseases of the urinary and respiratory systems;
- eye pathologies.
Self-administration of the procedure without the consent of the doctor is prohibited. Only a specialist can choose the optimal drug and determine the duration of the course of treatment.
Used drugs
During electrophoresis, various medications are administered to the child. Their choice depends on the disease to be cured.
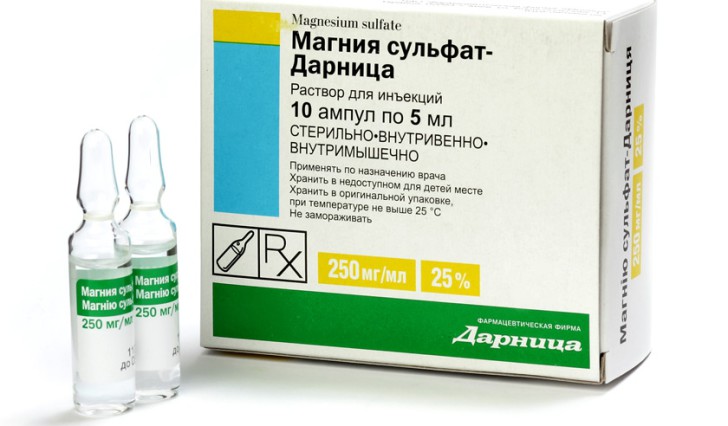
The medications used include:
- Magnesia. This drug effectively fights the pathologies of the respiratory system.
- Eufillin. It contains theophylline and ethylenediamine. The action of the drug is aimed at increasing diuresis, activating the work of the heart muscle and respiratory center, dilating blood vessels. Eufillin is able to increase blood circulation and destroy blood clots.
- Papaverine. The drug is included in the group of antispasmodics and effectively relieves spasms in the muscles.
- A nicotinic acid. This tool is a synthetic analogue of vitamin PP. It is used to improve carbohydrate metabolism, accelerate tissue healing and vasodilation.
- Calcium. It is indicated for paralysis and muscular dystrophy. In combination with vitamins of group C, the drug has a powerful anti-inflammatory and resolving effect.
- Dibazol. The tool is used to stimulate the spinal cord and strengthen the defenses of babies. It is widely used in the treatment of neurological pathologies and intestinal disorders. In addition, dibazol is effective with increased muscle tone. Prozerin and bromine have similar actions.
 Solutions of nicotinic acid and eufillin for electrophoresis
Solutions of nicotinic acid and eufillin for electrophoresis During the Ratner procedure, children are given electrophoresis with the simultaneous use of aminophylline and papaverine. This technique is intended for the treatment of birth injuries, cerebral palsy and blood flow disorders in the cervical spine.
Often, when conducting electrophoresis in babies, nicotinic acid and aminophylline are used together. The procedure helps with impaired muscle tone, hydrocephalus and birth injuries.
Procedure technique
Carrying out electrophoresis in babies is not difficult. Manipulation consists of several stages:
- A napkin or a piece of gauze is wetted with a solution of a drug, which is selected depending on the disease.
- The electrodes (plates) of the device intended for the procedure are wrapped with a cloth moistened with a medical solution and applied to the desired organ (collar zone, chest, lower back).
- The required impulse strength is set. Only after that the device is connected.
- Upon completion of these manipulations, the areas of the child's skin to which the electrodes were applied are wiped with a dry cloth.
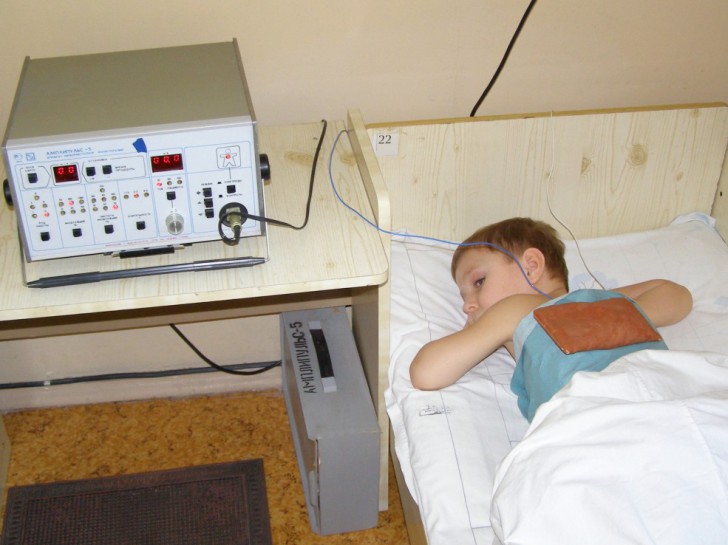
During the procedure, slight tingling of the skin is felt at the points of contact with the plates wrapped in a damp cloth, which can frighten a small patient. It is extremely important that one of the parents is nearby throughout the procedure. All metal objects (chain, cross, pendants, etc.) must be removed before the procedure to avoid burns.
Contraindications
Like any other medical manipulation, this physiotherapy has contraindications. These include:
- elevated temperature;
- tumors;
- heart and kidney failure;
- inflammation in the acute stage;
- predisposition to bleeding;
- blood clotting disorder;
- bronchial asthma;
- purulent skin diseases;
- dermatitis.
 The procedure has its own contraindications, so a thorough examination of the child is necessary.
The procedure has its own contraindications, so a thorough examination of the child is necessary. The procedure is prohibited in case of individual intolerance to the effects of current and the detection of an allergy to the drugs used. In the presence of damage to the skin in the places where the electrodes are attached, electrophoresis is postponed until complete healing.