Cervical osteochondrosis and arterial pressure. Can cervical osteochondrosis increase blood pressure?
About 70 percent of people are at risk of getting cervical osteochondrosis. This disease occurs at any age, but often in 20-40 years. Many people wonder if cervical osteochondrosis can increase blood pressure. Yes, in addition to the symptoms of acute pain, osteochondrosis of the neck is often the cause of the increase
Relationship between diseases
How are osteochondrosis and pressure related? Hypertension is an increase in the level of pressure that occurs in the systemic circulation. Most often, thirty percent of the world's population develops this disease in a chronic form. Given this and the fact that osteochondrosis occurs in about seventy percent of people, it becomes clear that the likelihood of a combination of these diseases is quite high. So, these ailments occur in approximately the same age group, and with increasing age, the number of patients increases significantly.
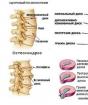
The cervical region is closely connected with the human vascular-cardiac system. So, the spinal sympathetic center, responsible for supplying the nerves, is located in the region from the 8th cervical vertebra to the 6th thoracic.
It can be said that osteochondrosis and pressure are interconnected. In addition, nerves located in the 6th thoracic and 3rd cervical vertebrae participate in the innervation of the heart muscle (supplying tissues or organs with nerves that provide continuous communication with the nervous central system). Therefore, any pathology that occurs in 3-5 cervical vertebrae disrupts normal blood circulation between the brain and spinal cord.
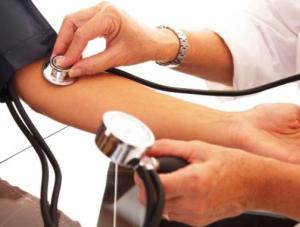
Today, doctors have determined that cervical osteochondrosis and blood pressure and heart rhythm disturbances have a strong relationship. As a rule, hypertension is found in patients who have protrusions and intervertebral hernias of the neck. Often in such a situation, the patient experiences constant pressure surges during the day.
Causes of pressure drops in osteochondrosis
There can be several reasons for the occurrence of hypertension. For example, during stress, its increase is a normal reaction of the human body (the survival of the human body is ensured, blood is sent to vital organs). But today, in a modern person, life is so full of various stresses that this fact often leads to a failure of defense mechanisms. As a result, we have an increase in the level of pressure even with a slight irritation.

So, in a person who is in a stressful state at an emotional level, in conditions of hypodynamia, it is the cervical region that is affected. Based on this, before drug treatment, if you have cervical osteochondrosis and your blood pressure jumps, a holistic examination should be carried out to identify reliable causes.
Symptoms of pressure drops in osteochondrosis
Hypertension is very often exacerbated by starvation of the brain, which occurs with a disease of the cervical region. This ailment is often found in the stage of exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the cervical region, in other words, with the formation of protrusions or intervertebral hernias. One of the main symptoms in this case are jumps or drops in pressure, that is, cervical osteochondrosis and blood pressure are associated, moreover, they are accompanied by dizziness and headaches.
In order to identify the involvement of pressure instability, it is necessary to carry out diagnostic procedures. But one of the effective methods is to study the symptoms at the time of an attack of drops. These include:
- dizziness and headache;
- dumbness of the fingers and shoulder girdle;
- pain in the neck.
In addition, an increase in pressure in cervical osteochondrosis is also accompanied by a sharp piercing pain and darkening in the eyes. If the pain does not go away when taking medications, then it is safe to say that the increase in pressure does not appear due to problems with the cardiovascular system and not under the influence of external factors, but precisely because of osteochondrosis.

If you observe the above symptoms in yourself, do not delay a visit to the doctor. Treatment of these ailments will help you get rid of discomfort and pain.
Cervical osteochondrosis and blood pressure: prevention
The best treatment for any disease is, of course, preventive measures. If it is already there, then you can alleviate your condition by softening the painful manifestations.
Methods for the prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
- Normalized loads. Be careful not to overload your body.
- Healthy and proper nutrition that does not result in metabolic disorders.
- Fresh air in the room. The room must be ventilated frequently, as a decrease in the oxygen content in the blood can cause vasospasm. Smoking leads to the same negative effect, so quitting smoking is an important step towards curing the pathology of the cervical region.
What you should pay attention to
Quite often, weather-dependent people attribute their headache to an increase in blood pressure and use drugs that reduce it. But the increase in pressure is more likely a consequence than the original cause. The pain caused by osteochondrosis leads to the fact that a person has a feeling of anxiety because of this, which leads to an increase in blood pressure. Therefore, drugs that reduce it do not help in this case, since the deficiency of blood flow in the cervical arteries is not eliminated.
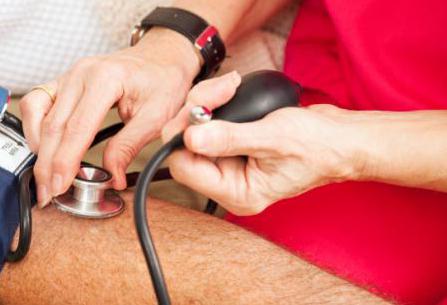
To avoid such situations, it is advisable for people who suffer from headaches to keep their blood pressure under control. To do this, measure it on weekends with good health - this will be considered your normal blood pressure. Then try to measure it every morning and evening. If you notice an increase, bring it back to normal by a method that is acceptable to you. If at the same time the pain has not gone away, then it can be assumed that the cause is osteochondrosis.
Cervical osteochondrosis and blood pressure: treatment
With the correct diagnosis of the ailments in question, the patient first of all expects drug treatment, which includes not only drugs that control pressure drops, but also those that have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Quite often, a patient who has an increase in pressure with cervical osteochondrosis is prescribed massage and therapeutic exercises. At home, it may be enough to perform preventive movements, tilts and self-massage in the neck every 2-3 hours. This simple method will reduce headaches and normalize blood pressure to some extent.
But you need to remember that active mobility or massage can cause an increase in blood pressure. Therefore, it is advised to perform all exercises and procedures under the supervision of a vertebrologist or a neurologist, since any slight deviation can lead to a drop or, on the contrary, an increase in pressure in osteochondrosis of the cervical region, thereby increasing the recovery and rehabilitation period.
Therapeutic exercises
Cervical osteochondrosis and blood pressure are diagnoses in which gymnastics is used, but it must be done systematically and regularly to achieve the full effect.
![]()
- Starting position - standing or sitting. As you exhale, tilt your head, bringing your chin as close to your chest as possible. Then slowly, as you inhale, turn your head as if you want to see your back. In the extreme position, linger for a couple of seconds and with an exhalation, slowly tilt your head to your chest again. Repeat exercise - 10 times. Based on your well-being, you can do several approaches 3-4 times, with an interval of about five minutes.
- Put your palm on your forehead and press on it for 15-20 seconds without tilting your head back.
- Starting position - lying on the stomach, hands - along the body with palms up. Put your chin on the floor plane and try to relax as much as possible. Slowly tilt your head to the right, trying to touch the floor with your ear. Return to original position. Then do the exercise on the left side. Repeat - 10 times.
The complex of recreational exercises should not include strong extensor and flexion movements of the neck, as they can injure the vertebral discs. Exercise should not be accompanied by pain. If you feel pain - reduce your load.