Violation of cerebral circulation in osteochondrosis of the cervical region: how to treat
A sudden loss of coordination, bouts of nausea and headache may indicate a violation of cerebral circulation in cervical osteochondrosis, the treatment of which should be started as early as possible. This ailment provokes a number of degenerative and pathological processes in the intervertebral discs and cartilage tissue, which entails restriction of mobility and disruption of the whole organism. Lack of timely therapy leads to stroke, coronary brain disease and other negative consequences.
What it is
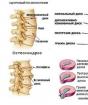
The cervical region contains seven vertebrae, which differ from each other in structural features and are relatively small in size. A high load falls on this section of the spinal column, since its main task is to ensure full mobility and support of the head. With cervical osteochondrosis, pinching of the vertebral arteries occurs, which leads to a lack of oxygen and impaired blood supply to the brain.
The connective tissue located directly between the vertebrae, with cervical osteochondrosis, undergoes dehydration and drying, which leads to compression of the vertebrae and pinching of nerve endings. Including squeezed and blood vessels responsible for the nutrition of the brain, resulting in a lack of nutrients and oxygen.

Causes of circulatory disorders
Violation of the blood supply to the brain in cervical osteochondrosis may be age-related or genetic in nature, or be a consequence of impaired metabolism. Hypertension, atherosclerosis, scoliosis, chronic fatigue, depressive states, disorders of the thyroid and endocrine systems also often act as provoking factors for local circulatory disorders.
Important! Lack of physical activity and low muscle tone are among the main causes of such disorders. At increased risk are people who lead a sedentary lifestyle and those engaged in monotonous sedentary work.
Symptoms
The first stages of osteochondrosis of the cervical region can proceed without pronounced symptoms, bringing the patient only periodic discomfort. However, in the absence of proper therapy, the disease progresses quite quickly and flows into the following stages, which are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Noise and ringing in the ears, accompanied by a feeling of fullness. In the case of a severe circulatory disturbance, patients often experience a deceptive feeling that water has entered the ears.
- Sudden loss of coordination and frequent dizziness may indicate a failure in the blood supply to the brain.
- Soreness of the eyes, aggravated by the movement of the eyeballs. Such symptoms are often the result of high stress at work, so it is worth visiting both a neurologist and an ophthalmologist.
- Headache is one of the most common symptoms that accompany a violation of the blood supply to the brain. Ignoring such a manifestation, using analgesics, is fraught with very negative consequences, up to a stroke and other serious problems with the vascular system.

In the event of a violation of the blood supply to the brain, patients often complain of numbness in individual limbs that occurs without any reason. The patient may experience a sensation of chills or heat with jumps in blood pressure. If the above symptoms are accompanied by tension in the muscles of the occipital part of the neck and head, discomfort and general weakness, then we can most likely talk about a failure in the local blood flow system.
It is important! In severe forms of impaired blood supply to the brain, the patient's consciousness may undergo temporary metamorphoses. This is expressed in jumps of activity, when a person abruptly passes from excessive excitement to a fainting state, or vice versa.
stages
Symptoms of cerebrovascular accidents vary depending on the stage of development. There are 3 stages in which the disease proceeds:
- The first stage, also known under the guise of discirculatory encephalopathy. At this stage, the patient is usually worried about general malaise and headache, accompanied by unsteady gait and sudden incoordination. If you do not begin to treat the disease at this stage, hearing begins to decline. The lack of oxygen and blood disrupts the functioning of the eye lenses, which leads to poor vision.
- Subcompensatory stage, at which neurological changes are pronounced. It is characterized by the appearance of an unsteady gait, bouts of nausea, problems with the vestibular apparatus, as well as a deterioration in the functioning of the speech apparatus and memory.
- At the third stage of circulatory disorders, a number of irreversible changes in the central nervous system occur, which entail the actual immobilization of the patient and the inability to serve himself independently.

If appropriate therapeutic measures are not taken in a timely manner, then such a problem can cause very serious complications. According to medical statistics, one fifth of cases of acute disorders of the blood supply to the brain ends in death. There is a high probability of disability, in which the patient loses the ability for analytical thinking, independent movement and orientation in the surrounding space.
Treatment of circulatory disorders
Therapy of such disorders is a rather complex task, the solution of which requires an integrated approach. It is necessary to start treatment directly with an examination by a therapist and a neurologist. To establish the most accurate diagnosis, the doctor must listen to the complaints of the patient himself, study in detail the history of his illness and the results of the tests.
In some cases, there is a need for an additional study using an ECG, MRI or X-ray of the cervical spine. What to do to improve blood circulation and prevent negative consequences?
- to establish the process of enrichment of the brain with oxygen;
- expand the lumen of blood vessels;
- restoration of intervertebral discs of the cervical spine;
- improving the properties of blood flow and its dilution.

Competent therapy should be aimed at restoring the full functioning of the spine, eliminating osteochondrosis and preventive measures to prevent recurrence of the disease. Conservative medicine involves taking painkillers up to novocaine blockade at the time of exacerbation. Anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal agents, chondroprotectors, nicotinic acid, muscle relaxants and vitamin complexes are also used.
Since taking pharmaceutical drugs causes some damage to the body, it is also worth using alternative methods of treatment. Manual therapy, acupuncture, reflexology, magnetotherapy, most traditional medicine recipes and other methods have a minimum number of side effects. At the same time, they can have a very positive effect on the patient's condition and slow down the development of the disease.
One of the main factors that play a significant role in recovery is daily physical activity. It is imperative to allocate time for hiking in the fresh air, as well as for therapeutic and orthopedic physical education.