Can pressure increase with cervical osteochondrosis?
Increased pressure in osteochondrosis is a dangerous symptom, since most patients struggle with it incorrectly. Instead of treating the cause, people treat the manifestation and harm their body even more.
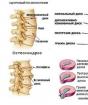
With osteochondrosis, the intervertebral discs are deformed and lose their elasticity, the vertebrae change their natural position. As a result, there are clamps on the arteries that provide blood circulation in the head. The body raises the pressure to oxygenate the brain. If at the same time the patient begins to artificially lower the pressure, the situation only worsens - the brain again loses the nutrition and oxygen it needs. Therefore, it is necessary to treat cervical osteochondrosis and pressure comprehensively if you do not want to harm yourself.
Doctors have proven that osteochondrosis negatively affects blood pressure. Pressure also begins to jump for reasons such as protrusions or intervertebral hernias of the neck. The pressure can rise or increase for several days in a row, and as a result, the patient suffers from a headache, numbness of the arms and shoulders, he is dizzy.
The neck contains a large number of blood vessels and nerves leading to the brain. As a result of spasms or a change in the position of the disc, the cervical arteries may be compressed. The brain stops getting enough nutrients and oxygen. The body is looking for a way out, and finds it in high pressure with osteochondrosis of the cervical region.
Blood pressure can rise if the brain needs increased blood supply, which suffers from osteochondrosis. The brain is the most important organ, and its tissues should not be allowed to starve. Sometimes the blood flow can be so compressed that the blood begins to pulsate as it passes through the obstruction. This is the most difficult case. An increase in pressure in osteochondrosis can also occur due to problems in the thoracic spine. There is also an artery here, the clamping of which can affect the pressure. Even a small amount of compression does.
- We advise you to read:
Blood pressure is a characteristic of blood circulation that affects human health and metabolism. When the pressure in cervical osteochondrosis changes, the following malfunctions in the body may occur:
- Boost. The clamp in the blood circulation speeds up the blood to nourish the brain cells;
- Downgrade. If high pressure has not brought the desired result to the body, it reduces the need for tissues in oxygen, inhibiting their condition;
- Changes within the skull. The most painful condition. In a normal state, the brain is in the fluid, which, among other things, circulates inside it. If the vessels are greatly dilated, they begin to compress the circulating tubules of the brain. In such cases, the pressure may increase, and the person begins to have a headache. To survive a critical state, the brain turns off some of its areas. Before, there is a strong weakness and pre-fainting. In extreme cases, the person faints;
- But most often, the pressure in osteochondrosis of the cervical region begins to change rapidly. The vessels then compresses, and the pressure rises, then it is released and the pressure returns to normal. Such a cycle can be repeated for a long time, which exhausts the body.
Those who do not know whether osteochondrosis can cause high blood pressure are simply trying to cope with hypertensive symptoms. They try to lower the indicator by any means and drink the appropriate medicines, sometimes they resort to traditional medicine. But if you simply lower the pressure when the brain lacks blood supply, things will get even worse. After all, high blood pressure is the body's way of coping with the lack of nutrition and oxygen in the brain cells.

Trying with all your might to artificially lower it, you further disrupt the functioning of the brain and risk becoming a victim:
- dizziness;
- Constant fatigue;
- Darkening before the eyes;
- doubling of vision;
- fainting state;
- Loss of consciousness.
Treatment
Before treating jumps, you need to find their cause. If the blood circulation changes from cervical osteochondrosis, you need to switch to complex measures. Drinking pills for hypertension is not enough here. Need to get rid of osteochondrosis.
Medications
Needs to be corrected. To do this, you need to have on hand drugs that dilate blood vessels. Unlike conventional blood pressure lowering drugs, they do not slow down blood flow, but increase the possible access of blood. As a result, the indicators go down, but the brain does not feel starvation. One of these drugs is Cavinton, which stabilizes the blood supply and metabolism of the brain.
Muscle relaxants, such as Mydocalm or Sirdalud, will help relieve muscle spasms. Excessive muscular tension often becomes the root of the problem of compressed vessels.

Pick up medicines that will deal with puffiness and inflammation. The blood in the veins stagnates, puffiness appears, pinching the arteries. Diuretics will help here. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibuprofen or Diclofenac, can help fight inflammation.
Chondroprotectors are used to help cartilage tissues regenerate and improve their metabolism. For example, Triaktiv or Moveks. Equator is a complex drug that combines Lisinopril and Amlodipine. Systemically fights with jumps in osteochondrosis. Reduces the risk of developing cardiac complications that may result from arterial occlusion.
- Be sure to read:
Physiotherapy
To get rid of the complications of osteochondrosis of the cervical region, osteochondrosis of the cervical region must be treated in a complex manner. Pharmaceutical products alone will not give the desired effect. It is necessary to strengthen and rehabilitate the body as a whole and the cervical region in particular:
- An orthopedic cervical corset will help reduce the load on weakened cervical muscles;
- The services of a chiropractor will correct the position of your vertebrae, release pinched vessels and nerves;
- Physical therapy classes will help stretch the spine and strengthen the muscles. The muscles will again take on the load, the spine will breathe freely. And stretching the spine helps free up the space between the vertebrae, freeing the pinched vessels and nerves. - sparing and effective variant of therapeutic exercises for osteochondrosis;
- Massage improves blood circulation in the problem area, stabilizing metabolic processes in the affected tissues. The muscles relax, and the spasms that compress the vessels, causing an increase in pressure, will go away.
Folk recipes
If the pressure threatens to rise with osteochondrosis, rub your neck with the following home rubs:
- Mix 10 ml of iodine, 10 ml of camphor oil, 300 ml of ethanol and ten tablets of crushed analgin. Let the rub lie down for twenty days in a place protected from light. Rub your neck - such an ointment, prepared at home, has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, stabilizes blood pressure;
- Ordinary St. John's wort oil can be used as an ointment, bath filler, or compress base.

- We recommend reading:
Prevention
If you have not yet learned from your own experience whether pressure rises with osteochondrosis, think about prevention:
- Get rid of extra pounds. The back muscles are not designed to constantly support a large body weight. When their strength is not enough, the vertebrae begin to squeeze the intervertebral discs, they are deformed, metabolic processes in them are disturbed;
- If your profession is related to the computer or you are a driver, try to get up as often as possible and do a little warm-up. Long sitting negatively affects the cartilaginous tissues of the discs;
- Don't lift weights, and if you do, do it with proper technique. Squat down, straighten your back and pick up the object;
- Do not chase sports records that the human body is not designed for normally;
- . Visit the pool, sessions of therapeutic exercises, stretching, yoga. If there is not enough time for this, just try to walk more often. So you strengthen the muscles, and avoid unnecessary stress on the intervertebral discs.
| Your feedback on the article |